Laptop computer
A laptop computer, also known as a laptop or notebook, is a portable computer that can easily be transported and used in a variety of locations. It often includes a flat LCD or LED computer screen installed on the interior of the upper cap of the clamshell form point. Laptops integrate enough of the typical components of a desktop computer, comprising a display, a keyboard, a pointing mechanism (such as a touchpad or trackpad), speakers, memory, a processor, and sometimes an optical disc drive used for storage or installing the software. Some laptops also have a touchscreen and/or a built-in camera.
This post contains affiliate links at no additional cost to you. I will be compensated if you buy after clicking the link.
Display
A display, also known as a screen or monitor, is an electronic visual display for computers. The most common display device in a laptop is a liquid crystal display (LCD), which uses a backlight to illuminate the pixels and create an image. Some high-end laptops also use an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display, which does not require a backlight and can offer deeper blacks and more vibrant colors.
The resolution of a display is the number of pixels in the horizontal and vertical dimensions and is typically measured in pixels per inch (PPI). A higher resolution means that more pixels are packed into the same screen size, resulting in a sharper, more detailed image.
The aspect ratio of the display is the proportion of the width to the height of the screen. The most common aspect ratio for laptops is 16:9, which is the same as a standard HDTV. Some laptops feature a 3:2 aspect ratio, which is taller and provide more vertical space for productivity work.
Refresh rate is the number of times per second that a display updates its image, measured in hertz (Hz). A higher refresh rate means that the image on the screen will appear smoother and more fluid.
Keyboard
A keyboard is an input device for a laptop computer that contains keys for typing text and numbers, as well as special keys for controlling various functions of the computer. A typical laptop keyboard includes letters, numbers, and punctuation keys, as well as function keys, control keys, and cursor movement keys. Some laptops also include a numeric keypad, which is a separate set of keys for entering numerical data quickly.
Some keyboards have a backlight feature that allows using the keyboard in low-light conditions.
Laptop keyboards can vary in terms of the layout and size of the keys, and the amount of travel and tactile feedback they provide. Some users prefer the feel of a traditional mechanical keyboard, while others prefer the slim profile and quiet operation of a chiclet-style keyboard. Some high-end laptops feature a keyboard with a touchpad integrated into the keyboard, often called a Touch-type keyboard.
Some users also prefer to use an external keyboard with their laptops for a better typing experience, and ergonomics or to use a keyboard with a specific layout like Dvorak or Colemak.
Pointing device (such as a touchpad or trackpad)
A pointing device is an input device used to control the movement of a cursor or pointer on a computer screen. The most common pointing device in a laptop is the touchpad, which is a flat, touch-sensitive surface that is integrated into the laptop's keyboard. Users can move the cursor by sliding their fingers across the touchpad and can perform clicks and other actions by tapping or swiping on the touchpad. Some touchpads also support multi-touch gestures, such as pinch-to-zoom, which allows users to zoom in and out of images and documents.
Another type of pointing device commonly found in laptops is the pointing stick, also known as a Trackpoint. It is a small, rubberized nub located in the center of the keyboard. Users can move the cursor by applying pressure to the stick in the desired direction and can perform clicks by pressing down on the stick.
Some high-end laptops also include a trackpad with a built-in fingerprint reader, which allows users to quickly and securely log in to their computers using their fingerprints.
Some users prefer to use an external pointing device such as a mouse, trackball, or a stylus with their laptops for better control, and ergonomics or to use a specific type of pointing device that they are comfortable with.
Speakers
Speakers are a device that converts electrical audio signals into sound waves, allowing the user to hear sound from their laptop. Laptops typically have built-in speakers that are located on the bottom, sides, or front of the computer. The quality of the speakers can vary widely between different laptop models, with some providing rich, full sound, and others producing weaker, tinny sound.
Some laptops have stereo speakers, which means that there are separate speakers for the left and right channels of the audio. This allows for a more immersive and realistic listening experience, with a sound that appears to come from different directions.
Some high-end laptops also have surround sound speakers, which simulate a surround sound experience, that can be used for gaming or watching movies.
Some laptops also have a built-in subwoofer, which is a speaker designed to produce low-frequency sound, such as bass. This can improve the overall sound quality of the laptop by providing more powerful and nuanced bass.
Users can also connect external speakers to their laptops through the audio jack or Bluetooth. This allows them to use high-quality speakers that are designed for a specific type of music or sound, or to use speakers that are larger and more powerful than the built-in speakers of the laptop.
Memory
Memory, also known as RAM (Random Access Memory), is a type of computer storage that is used to temporarily store data that a computer is currently using or processing. In a laptop, memory is typically installed on small, rectangular chips called DIMMs (Dual In-line Memory Modules) that plug into the motherboard.
The amount of memory in a laptop is measured in gigabytes (GB) or terabytes (TB). The more memory a laptop has, the more programs and tasks it can handle at the same time without slowing down. A laptop with 4GB to 8GB of memory is sufficient for most everyday tasks such as web browsing, office work, and streaming. However, for more demanding tasks such as gaming, video editing, or running multiple programs at the same time, 16GB or more is recommended.
The memory speed is measured in MHz (Megahertz) or GHz (Gigahertz). A higher speed means that the memory can transfer data to the CPU more quickly, which can result in faster performance.
It is also possible to upgrade a laptop's memory by adding additional DIMMs, but it is important to check the maximum amount of memory that the laptop's motherboard can support, as well as the type of memory (DDR3, DDR4, etc.) that is compatible with the laptop before purchasing new memory.
It is also worth noting that a laptop has built-in storage, usually a hard drive or an SSD (solid state drive) where it stores the files and programs, but it is not the same as memory and it's used for long-term storage.
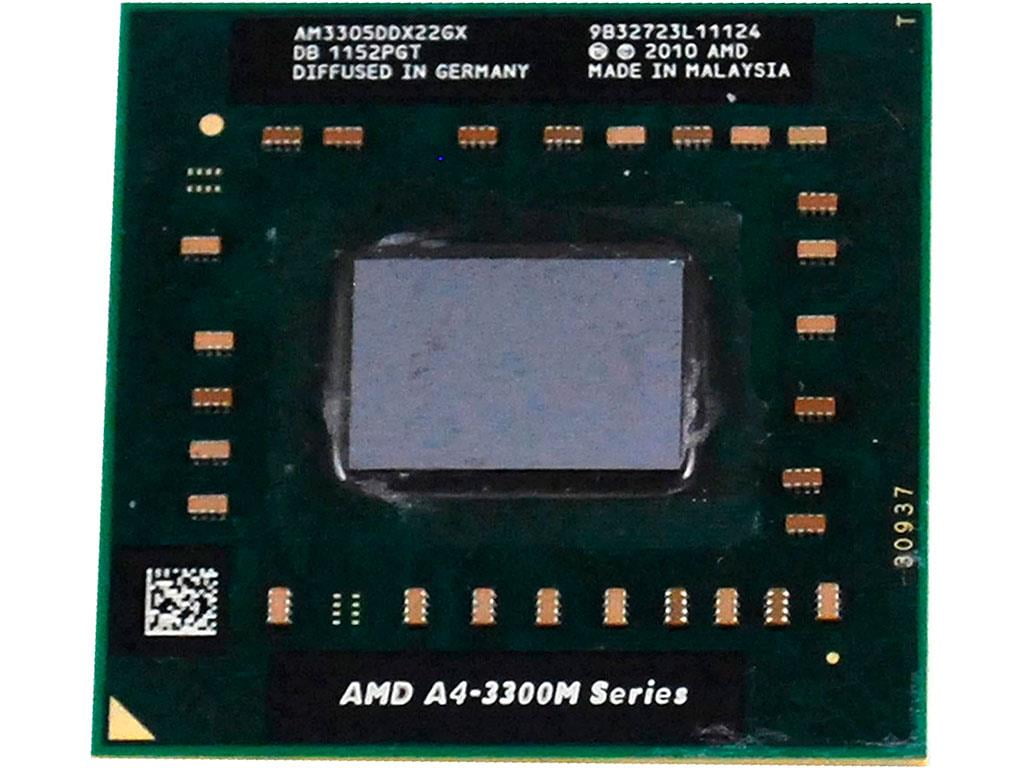
Processor
A processor, also known as a Central Processing Unit (CPU), is the brain of a computer and is responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. In a laptop, the processor is a small, compact chip that is soldered to the motherboard.
The performance of a processor is measured in clock speed, measured in GHz (gigahertz). A higher clock speed means that the processor can execute instructions more quickly. It's also important to note that not all GHz are created equal, as some different architectures and designs can affect performance.
Another important factor in the processor's performance is the number of cores. A core is a processing unit, and the more cores a processor has, the more instructions it can execute at the same time, which can result in faster performance.
There are different types of processors available for laptops, the most common ones are from Intel and AMD. Intel processors are known for their high performance and power efficiency, while AMD processors are known for their affordability and good performance per dollar.
The choice of a processor depends on the intended use of the laptop, for basic tasks such as web browsing and office work, a dual-core processor with a clock speed of 2.0GHz or more is sufficient. However, for more demanding tasks such as gaming, video editing, or running multiple programs at the same time, a quad-core or higher processor with a clock speed of 3.0GHz or more is recommended.
It's also worth noting that it's not possible to upgrade a laptop's processor, so it's important to choose a processor that will meet the needs of the intended use of the laptop.


No comments:
Post a Comment